American scientists David Julius and Ardem Patapoutian have been honored with the Nobel Prize in the field of Medicine for the year 2021. The duo has won this award for their research in the domain of somatosensation, pertaining to receptors responsible for sensing touch, heat/cold and pain. The discovery of these receptors is likely to deeply influence how chronic pain disorders are treated.
The two scientists have helped the medical community to discover the basic molecular mechanism of temperature and touch perception by our bodies. This has opened new horizons in the domain of practical chemistry, which would enable tweaking, suppressing and activation of individual cells/genes and molecular pathways to suppress pain or physical sensation.
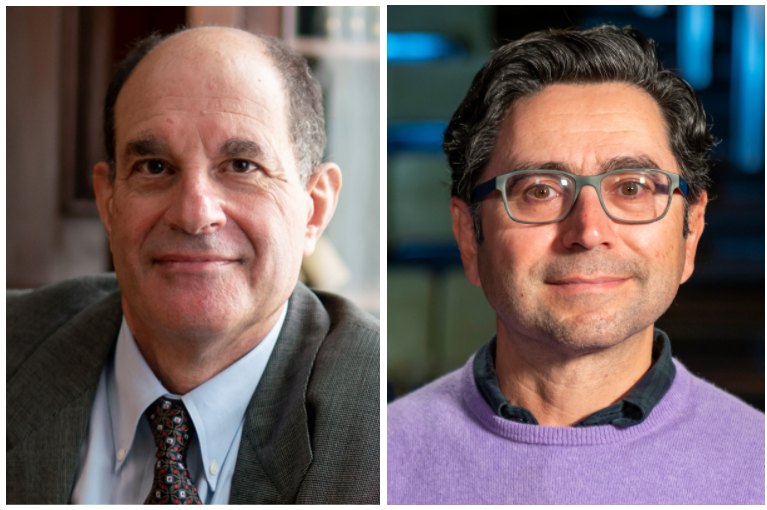

As per Nobel Assembly at Sweden’s Karolinska Institute, the work of the two scientists has helped elucidate the mechanism of conversion of physical sensations of heat or touch into nerve impulses that enable the brain to comprehend and adapt to our surroundings.
Ardem, born in 1967, hails from an Albanian family. However, he spent most of his youth in Los Angeles, US. Patapoutian is currently serving as a professor at Scripps Research, California. Formerly, he was associated with the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena and the University of California, San Francisco.
“In science many times it is the things we take for granted that are of high interest. This knowledge is being used to develop treatments for a wide range of disease conditions, including chronic pain”, said the Nobel Prize winner.
Ardem’s major contribution was to discover the cellular mechanism, as well as the core gene(s) (Piezo1 and Piezo2) responsible for converting the mechanical pressure exerted on the skin into an electric nerve impulse.
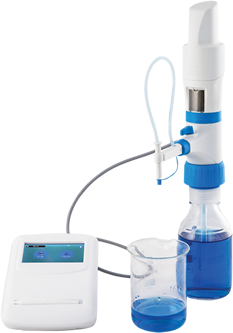
David Julius was born in New York, and is currently a Professor at the University of California, San Francisco, (previously was associated with Columbia University, New York). He was interested in finding out the role of natural products in identifying biological functions. In his research, he used Capsaicin, a molecule responsible for inducing a false stimulus of heat in the consumption of chili peppers. This helped him understand how a novel ion channel protein, later called TRPV1, enables the skin to sense different temperatures. With his work, he hopes to unravel novel treatment options for the treatment of chronic pain disorders.
This research work led to the discovery of several other protein receptors, sensitive to hot and cold temperatures. For instance, TRPM8 is a skin receptor that gets activated in low-temperature conditions. The gene was discovered using menthol as stimuli. Presently, several genes, including TRPM2, TRPM3 and TRPA1 have been discovered which are directly linked to temperature sensing.
“We all know there’s a real lack of drugs and approaches to treat chronic pain. I think we need some new insights and new ideas for treating pain, pharmacologically and other ways, and I think our work will contribute to that”, said Julius in a UCSF’s Youtube video posted in 2017.
What is the meaning of Somatosensation?
When talking about sensory impulses, we mostly think of the senses associated with sight, taste, touch, smell and hearing. However, the sensory perceptions related to touch are quite complex and we know little about how temperature and pain is perceived by the body. The sensations associated with hot and cold objects, the ability to identify an object only through touch, maintaining the balance on a beam- all of this can be related to somatosensation. In addition, the somatosensory system is known to regulate various internal physical processes, such as respiration, bone restoration, maintenance of blood pressure, and urination.
Somatosensation is slightly different from other kinds of stimuli. For instance, receptors in other sense organs are localized, such as retinas in the eyes, tongue for taste and cochlea in the ears. On the other hand, somatosensory receptors are present throughout different parts of the body, including the skin, muscles, bones, joints and internal organs.
How do Somatosensory Receptors Work?
As per Julius’ and Patapoutian’s research, somatosensory receptors are basically ion channels. These channels are stimulated by temperature, a chemical compound or any type of mechanical pressure. The sensations enable the channels to open up, thus allowing the flow of charged particles (electrical signals) into the neuron. It has also been established that different somatosensory receptors respond variedly to different ranges of temperature and pressure. For example, different receptors are responsible for perceiving a heavy blow versus a gentle touch. Some scientists are also trying to discern the role of somatosensory signals in providing a sense of conscious selfhood.
Jan Adams, the chief science officer at Gruenenthal, a German pharmaceutical firm specializing in chronic pain therapies, said that the research had “opened up a whole new field of research for new non-opioid pain therapies.”
According to reports, both Nobel laureates were totally unaware of this development. The Nobel Prize money was divided equally among both the awardees.




 6443
6443