Types of Micropipette can be classified depending upon:
- As per the Working Principle
- Air Displacement Micropipette: In an air displacement pipette, a small air cushion exists between the piston and the liquid solution during the process. These pipettes are extremely precise for a wide range of piping applications.
- Positive Displace Micropipette: With a positive displacement pipette, a piston replaces the air cushion and glides along the inner edges of the capillary for easy pipetting of viscous, dense and surfactant liquids.
- As per Operation Mechanism
- Mechanical Micropipette: These micropipettes are manually operated based on a piston-shaft spring mechanism.
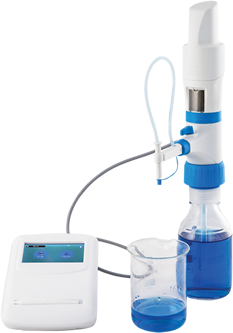
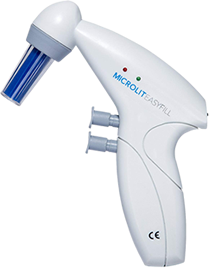
- Electronic Micropipette: Electronic micropipettes are more accurate than pipetting manually and mostly automated. Electronic pipettes remove the hand control one has over the pipette. The volume is set electronically, and with the push of a button, the plunger moves up and down electronically, leaving no room for human error.
- As per the number of Channels
- Single-Channel Micropipette: A single-channel micropipette is one that has a single channel to aspirate or dispense the liquid.
- Multi-Channel Micropipette: A multi-channel micropipette has multiple channels to aspirate or dispense the liquid. It is commonly available in 8-channel, 12-channel and 16-channel variants.
- As per Volume or Capacity
- Fixed Volume Micropipette: In a fixed volume Micropipette, the volume of the liquid to be aspirated or dispensed remains constant. These micropipettes are used when the same amount of liquid has to be dispensed multiple times.
- Variable Volume Micropipette: This micropipette comes with a specific minimum and maximum volume range. The amount of liquid to be aspirated or dispensed can be adjusted (within the volume limit of the micropipette) based on the user’s requirement.
Understanding the different types of micropipette such as fixed volume, adjustable volume, and multichannel—allows researchers to choose the right instrument for their specific needs, whether it’s routine pipetting tasks or high-throughput applications.




 5573
5573